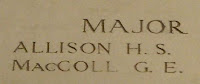A number of the Allisons
who settled across Northern Ireland became physicians. Hazlett Allison (1851-1925), named for his
mother Rachel Hazlett, was born at Drumnaha, the same farm that had been in the
Allison family for generations. He became
a doctor and joined the Indian Medical Service.
He and his wife Mary had three sons and one daughter. Their first child, Hazlett Samuel Allison
(1894-1917) was born at Fort St. George (now known as Chennai) in Madras (now
Tamil Nadu), India. Fort St. George was
the administrative seat of British power in India and was built in the 1600s as
the first British settlement in India.
It was rebuilt in the mid-1700s and is now used as an administrative building
for the state legislature of Tamil Nadu.
 |
| Fort St. George |
In 1873, Hazlett
Allison joined the Indian Medical Service as a surgeon, arriving at Fort St.
George in 1874 where he took up his post.
He rose to the rank of Lieutenant Colonel, distinguishing himself as a
Professor of Anatomy at the medical college and became a fellow at Madras
University in August 1892. In June 1891,
Hazlett married Mary Hunter Woods, and they both went to live in India. It was
while he was posted in Madras that Hazlett and Mary welcomed their first child,
Hazlett Samuel Allison, born in 1894. From
July 1901 to December 1903, when he retired, Lt-Col. Hazlett Allison was the
surgeon general at the hospital in Madras (records indicate the family had
already re-settled in Ireland in 1901 by the time of Lt.-Col. Allison’s
retirement).
Hazlett Samuel spent
his first years in India before his parents returned to their home in The
Shola, Portrush, Ireland in 1901. Noreen
Mullan, a local historian, has written an account of Hazlett Samuel Allison’s
life and notes that at the age of 10, young Hazlett entered school at Campbell
College Belfast. The school was still quite
new, having been established in 1894, and was at that time primarily a formal
boarding school, with significant grounds and facilities, located near the
Northern Irish Parliament at Stormont. He
graduated in 1911 and that same year entered Jesus College Cambridge.
By all accounts,
Hazlett Samuel was an athlete, demonstrating prowess in rugby and golf. While he didn’t continue in rugby while at
Cambridge, he did continue to indulge in his passion for golf. N.Mullan’s account includes a golfing
incident that made it into the local papers.
The incident took place in 1913 in the final round of the President’s
Cup, a foursome competition. The team
was reportedly Mr Lloyd Campbell / Mr H V Coates and Mr H S Allison / Mr R A
Cramsie. The local paper reported:
The players were all
square playing to the seventeenth (or gasworks) hole, approaching which the
ball driven by Mr Allison wedged between the wire netting, which is placed
round the green to prevent balls going out of bounds, and the top or guiding
wire of the fence. The local rule says
that a ball outside the fence is out of bounds, and the rules of golf on the
subject are that a ball is "out of bounds" when the greater part of
it lies within a prohibited area. In
this case the ball was exactly centred; and a diagram has been drawn by Mr
Vint, the secretary, showing the exact position of the ball, with explanatory
notes, to be forwarded to the golfing authorities for decision. If it is held that the ball was within
bounds, Mr H S Allison and Mr R A Cramsie would be the winners by one
hole. After the incident above described
two further holes were played, each of which were ties.
At both Jesus
College and at Campbell College, Hazlett Samuel was part of the Officer Training
Corps (OTC), which would not be unusual for students, and certainly not for
someone like Hazlett Samuel whose father was himself a member of the British
military.
 In 1914, Hazlett
Samuel Allison graduated with his B.A. from Jesus College Cambridge. His intent was to follow his father in
medical studies, and he wrote his first exam for medical school the year of his
graduation - the same year the war broke out.
At the age of 20, having spent his formative years in Madras surrounded by soldiers, and training with the OTC since he began his
education in Ireland, Hazlett Samuel Allison must have felt duty-bound to
join up. He enlisted on August 8, 1914
and was given the position of Second Lieutenant to the Royal Irish Rifles (‘D’
Company, 7th Battalion). Before the end
of the year he rose to Lieutenant. His
Battalion was posted to the French theatre of war in December 1915. In April 1916 he had gained the rank of
Captain and that December, Major. At
that time, he was one of the youngest Majors in the Army.
In 1914, Hazlett
Samuel Allison graduated with his B.A. from Jesus College Cambridge. His intent was to follow his father in
medical studies, and he wrote his first exam for medical school the year of his
graduation - the same year the war broke out.
At the age of 20, having spent his formative years in Madras surrounded by soldiers, and training with the OTC since he began his
education in Ireland, Hazlett Samuel Allison must have felt duty-bound to
join up. He enlisted on August 8, 1914
and was given the position of Second Lieutenant to the Royal Irish Rifles (‘D’
Company, 7th Battalion). Before the end
of the year he rose to Lieutenant. His
Battalion was posted to the French theatre of war in December 1915. In April 1916 he had gained the rank of
Captain and that December, Major. At
that time, he was one of the youngest Majors in the Army.
His rise in the
ranks was due to extraordinary courage and initiative, evidenced by the war
diaries and by his mention in despatches.
On the night of June 27, 1916, the 7th Irish were in the
trenches in Hulluch, France. Then
Captain Allison and another officer, 2nd Lieutenant M.J. Hartery, left
the camp and crossed the enemy’s wire to look for gaps. Their inspection revealed no gaps, but a spot
along the wire which was thin and able to be cut. Soon enough they were seen and fired upon, so
returned to camp with their report. The
enemy fire at the camp was reportedly weak and erratic, so a couple of days
later, Captain Allison commanded another patrol which was mentioned in
Despatches in the London Gazette on 4 January 1917. The Despatch commended Capt. Allison for
gallant and distinguished service in the field.
The official record says:
Near Hulluch, on the
night of 31 July - 1 Aug, he was in charge of an enterprise against the German
trenches. Shortly after the return of his party, the enemy made a bombing
attack on our saps. Capt. Allison immediately returned to the saps and
organized a counter-attack, which not only drove off the Germans, but followed
them up and bombed them back into their own trenches. During the past nine
months Capt. Allison has repeatedly shown great courage and resource whilst
leading patrols, and has set a splendid example to all ranks.
 |
| Article from Weekly Telegraph November 25, 1916 p.7 |
There were five major offensives at Ypres, Belgium. The army was seeking to take high ground and eventually take back this northern part of France, Belgium and Holland. The attacks would ultimately lead to the battle at Passchendaele. By the summer of 1917 when Major Hazlett Samuel Allison and the Royal Irish Rifles marched in, the Battle for Messines was about to commence.
The war diaries of
the 7th/8th Battalion recount movements in and around
Ypres, through trenches, to small towns to train, bathe and be inspected, get
prepared for offensives, and be subjected to constant shelling and artillery
fire that was unpredictable in its intensity.
Over the course of that summer leading to the battle at Passchendaele, the
weather deteriorated and the trenches became soaked, the field mud, and any
effort at attack gained inches at best.
On May 16, 1917, Major
Allison left on leave, returning May 30 when his Battalion was stationed at
Butterfly Farm. Just two nights before, the Farm had been subjected to heavy shelling, resulting in two wounded
and one soldier suffering from shell shock.
At the end of May, the unit’s strength was 40 officers and 940 other ranks.
The first week of
June, the 7th Battalion was issued Order Number 118 (June 6, 1917). The Battalion was to be part of the Battle of
Messines:
Whilst moving to
assembly position and when finally in position, every care is to be taken to
avoid arousing the suspicions of the enemy.
Smoking, striking of matches, flashing of torches and unnecessary talking
are forbidden.
The Battle at
Messines was intended to draw German troops away from the embattled French forces
and capture German defences on the ridge that ran through Messines and
Wytschaete. This would allow the British
a high ground from which to command their attack on Passchendaele, and
ultimately drive the army up the coast to Holland. It was a first strike preparing for the Third
Battle of Ypres in July. In the Battle
of Messines, the troops were to use a creeping barrage, which is a slow moving
artillery attack which provides cover for infantry behind it. In this case, the attack would start with
mines.
The Royal Irish were
to provide Brigade Support on the right and left of the attack on Gil Trench (the
Mauve Line). They would take over in the
event the attacking 9th Royal Dublin Fusiliers became otherwise
engaged. Royal Irish were to move to a position
at Vierstraat Switch. Once the Mauve Line
was taken, they would need to work quickly to consolidate their line. Having received their orders, the Battalion
prepared for the assault. The evening of
June 6, the Battalion was inspected at their position opposite Wytschaete. They marched to their position opposite Vierstraat
Switch, arriving by 2 am. 3:10 am was zero
hour. The mines went up, artillery opened
fire and the attack commenced.
By 8 am, the
Battalion received orders to move to the Chinese Wall, which took them an hour
and a half, and they remained there through the day. The fighting was intense,
but the German defence had been devastated by the mines and shelling. The Irish Rifles as part of a larger force
were able to take their objectives as the remaining German forces eventually either
surrendered or retreated. On June 8, the
battalion relieved the 47th brigade on the Black and Blue lines and
installed their battalion headquarters in a dugout in Wytschaete Wood. The Battalion was later relieved and moved to
Vierstraat Switch with HQ at The Ribb.
It wasn’t until June
11, after four intense days of fighting, that the Battalion was withdrawn from
the line and marched to Clare Camp. Throughout
June, the Battalion engaged in the cycle of trench warfare: marching, billets,
parades, inspections, training, and fighting.
On June 29, they arrived at Rubrouk for much needed baths. At the end of June, the battalion strength
was 39 officers and 969 other ranks. The
Battalion had lost an officer when their HQ was hit with artillery fire.
The Commonwealth forces
had managed to take the Messines Ridge in June, but then started a long slog through
trenches with little gain. July was much the same as June, with weather getting
worse, affecting trenches and the ability to make any ground forward. On July 26, 1917, Major Allison and some other
officers left Camp Watou Area No 1 to reconnoitre the front. On July 30, the Battalion was getting ready as
corps reserve (order No 129). The Third
Battle of Ypres was about to start. This
battle was intended to move closer to Passchendaele by taking the ridges south
and east of Ypres. The Royal Irish were
in their ready position on July 31 at 11 p.m.
At 3:40 am the battle commenced.
 |
| Excerpt of trench map showing Frost House and Frezenberg |
The battalion was attached to the 44th Infantry brigade for the attack. Under heavy fire, the Battalion was in
position on August 1 waiting for relief, when at 6 pm they heard that they
would not be relieved until the situation in front was “cleaner”. They received orders to stand and be ready to
hold the German front back. The commanding
officer understood that the Germans may have broken through north of Frost House.
The orders to remain
and hold the position continued through August 2. At 4 am that morning the Battalion was
ordered to send out guides to bring back the 47th Brigade from a
meeting point at Potijze Chateau. The
guides went out as ordered, but no battalion showed up for them to guide back. Finally, at 2:10 pm that day, the battalion
was ordered back Toronto Camp, arriving at 7:15 pm after three exhausting days
of fighting. But they were never far
from danger. After a rest and baths,
they marched to railways near Brandhoe and then continued on to Ecole. There was often artillery fire, and on August
7 they were heavily shelled. They arrived
at Frezenberg Redoubt to continuous bombardment. On August 8 the Battalion HQ was hit and
everyone who was in there at the time was either killed or wounded.
It was here, at
Frezenberg Redoubt, after a week of heavy fighting, marching, exhaustion and confusing
orders that Major Hazlett Samuel Allison of B company was killed – August 9, 1917. He was buried nearby, but the location of his
grave was never found again. His company
had to leave him behind when, on August 15, they headed to the trenches to join
in the attack on Frezenberg Ridge.
The Passchendaele Archives
describes Major Allison’s death:
On 7 August 1917 the
7th Battalion Royal Irish Rifles (48th Brigade, 16th Division) marched to the
frontline and relieved the 2nd Battalion Royal Dublin Fusiliers. D Company was
positioned on the left of the Ypres-Roulers Railway, near Frezenberg. The next day
the Germans shelled the frontline during the whole day. They hit the battalion
Headquarters, killing or wounding all the runners and observers. On 9 August
1917 Major Allison was killed, probably by a shell. He was buried near to the
place where he was killed, but afterwards his body was never found.
 |
| excerpt from Battalion war diaries showing entry for Major Allison's death |
Before the Third
Battle of Ypres, at the beginning of August, the Battalion counted 36 Officers
and 862 other ranks. By the end of the
month, there were 18 officers and 606 other ranks. The month had been devastating not just for
Major Allison, but for so many who died in the fighting: the 7th Battalion of the Royal Irish Rifles was not the only one that had suffered significant loss: the official total of losses for British Commonwealth forces numbered greater than 244,000.
Major Allison was awarded
the 1914-15 Star, the British War Medal, and Victory Medal, all of which were
sent to his father at The Sholes, Portrush, Ireland on September 12, 1919.
Hazlett Samuel Allison
did not live to see the victory at Passchendaele, which occurred in November,
but his contribution to this fight is commemorated at the Menin Gate.
 |
| Menin Gate Ieper. Above right, inscription on Panel 40. |
Every evening at the
Menin Gate in Ieper, The Last Post is sounded in memory of the thousands whose
names are engraved on the panels inside the memorial. These are names of those without graves who
died between October 1914 and October 1918 in Belgium, including Major H.S.
Allison.
Major Allison is also remembered at memorials through Jesus College Cambridge, Irelands War Memorial Records 1914 – 1918, Portrush War Memorial, Holy Trinity Church, Portrush, Campbell College, Belfast, and at the Family Grave, Ballywillan (Old) Graveyard.
On this Remembrance
Day 2019, I will remember Major Hazlett Samuel Allison of the 7th
Battalion, Royal Irish Rifles – born in India, excelled in College, a keen
rugby player and talented and committed golfer, and an extraordinary officer.
 |
| From UK, De Ruvigny's Roll of Honour, 1914-1919, p.5 |
References and acknowledgments:
Thanks to Noreen
Mullan for her excellent research and some photos (used with permission), and
to Dr. James Allison for his contributions.
Trench maps National
Library of Scotland. https://maps.nls.uk/
De Ruvigny’s Roll of
Honour, 1914-1919 p.5
Original War Diary 7th
Battalion Royal Irish Fusiliers
Images of Menin Gate
used in this article are originals.
Please seek permission to re-use.
Image of HS Allison
memorial at Menin Gate: http://www.instgreatwar.com/page17.htm
Mention in Despatch
available at: https://discovery.nationalarchives.gov.uk/details/r/5beca90e-bb8b-4ae7-86fd-16c6edc893e2
Jon Sandison’s article
about his visit to the Menin Gate:
http://www.scotlandswar.co.uk/pdf_At_The_Menin_Gate.pdf
Menin Gate in
photos: http://thebignote.com/2014/11/03/the-menin-gate-memorial-to-the-missing/